
What is on-page SEO?
On-page SEO generally accounts for everything you can be doing on your own website to optimise it.
This generally focusses on 6 key areas:
- Headings and page titles
- General written content
- URLs
- Internal links and site navigation
- Alt text
- Meta titles, tags and descriptions
Off-page SEO then deals with optimisation away from your website itself. I’m not an expert in this area, but it’s about gaining backlinks, using certain tactics on social media, and also ensuring you are doing everything you can to ensure Google is indexing your site correctly, including uploading site maps and requesting crawls…I believe!
In this blog, I’ll explain each of the main areas of on-page optimisation and some quick win tips for improving each one.
Headings and page titles
The best way to optimise your on-page SEO is to carefully check all of the main headings or titles of your pages. These can be different things, but for most templates the ‘main title’ at ‘the top of a webpage’ is the H1 Heading.
<H1> is a tag given to this heading and if you could see the HTML code for this page you’d find the title surrounded by this symbol. This indicates to a search engine that it is one of the most important bits of information on that page. It’s the main label,
For many business owners, their main headings and/or page titles might be ‘About’, ‘Services’, ‘Contact’. Whilst this is clear and familiar to website visitors, it doesn’t help Google identify what the page is about.
SEO TIPS
- Check all of your H1 headings and page titles – can you improve them with keywords?
- Ensure there are no duplicates.
- Make them as unique, as possible.
General written content
As well as <H1> tags, every subsequent headings is also given a tag, i.e. <H2>, <H3>, <H4> and so on. Then, your normal body of text is given a <p> tag. My understanding is that this is the approximate order in which Google ‘scans’ your site. So, to optimise your site you want to be thinking carefully about what you are putting in headings and subheadings at the different levels, as well as the content in your main paragraphs or sections.
Remember that Google still ranks based on E-A-T, which means Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness too. My recommendation is always that quality content comes before anything else. High quality content is clear and easy to follow. It’s well broken up with headings and tells the website visitor exactly what they want to know, i.e. they find exactly what they are expecting to find.
SEO TIPS
- Check the tags (or formatting) for all of your subheadings.
- Ensure subheadings are keyword rich, without losing sense or quality.
- Read any longer paragraphs out loud to ensure they are clear and flow well.
- Check all content on different size screens to see if any appear particularly long and cumbersome.
- Check the content on a page fits logically with the page title and headings.
URLs
Again, depending on who designed your website or how it was developed, the URL of a specific webpage is likely to be drawn from the page title (and sometimes the automatic <H1> heading). Consider if the address given is the best URL for the page.
Gone are the days of keyword stuffing URLs, no more www.thecontentconsultancy.com/hampshire-copywriter-website-services thankfully! However, you can be more creative than: www.thecontentconsultancy.com/services
Another thing to watch out for, which can penalise you in the search results, is replicated URLs. For example, they simply have the addition of a number, i.e. www.thecontentconsultancy.com/services-1 . This can happen automatically if you clone or duplicate a webpage, but forget to update the URL and make it unique. This confuses a search engine!
Remember – you want to make a search engine bots life as easy as possible!
SEO TIPS
- Step through each page of your website paying careful attention to the URLs.
- Correct any duplications or very similar URLs.
- Identify opportunities to add keywords, if appropriate.
Internal links and site navigation
Utilising internal links and having a clear site navigation is a good on-page SEO tool.
It’s not just about Google, however, this is about giving your website visitor a great experience, which in turn is likely to keep them on your website for longer, which in turns tells Google this is a good, valuable and trustworthy site.
Make sure that you have links between all of your pages. This includes not only hyperlinks and buttons between pages, but also pages included in relevant menus. Orphan pages (i.e. those not linked to for anywhere) are fine for specific landing or sales pages, but don’t accidentally leave something out if that is not their role.
Linking to certain pages frequently across your site should drive traffic there and alerts Google to the significance of that page. Be aware of this when you are considering your calls to action. If every button sends your website visitor to the contact page, for example, make sure there is enough content on there to give a search engine a clear understanding about what this page is and ensure it indicates what you do as a business and what you are about.
SEO TIPS
- Audit your website and the number of interlinks on each page (including hyperlinks and call to action buttons) as well as where they point to.
- Check ease of navigation – set yourself or another the task of finding certain information or items on your website starting from a certain location (i.e. your homepage) – if they find everything within 3 clicks then the site navigation and lay out are working well. If they are taking more, consider your website structure.
Alt text
I am passionate about alt text – it’s a weird thing to say for a copywriter I know, but it’s actually not about the SEO. It’s about the importance of accessibility. I don’t know what it is like to be blind or visually impaired, but I badly short sighted. And without my contact lenses or glasses, the world is a complete blur, and this can be very unnerving when I am somewhere unfamiliar.
Alt text relates to the text you can use to accompany any images on your site. Most good websites include lots of imagery – both photos and illustration – so ensure the fields marked alt text are filled in. These are often found in your media library when you click on a certain image. Even if it’s not high quality copywriting – simply describe the contents of the images – it’s important to support everyone to access all elements of your website.
Furthermore, avoid uploading photos that have file names like 1938495868.jpg – rename them with a clear title, and there’s no reason why they can’t include the name of your business and the relevant service and/or product category. Filenames are also scanned by search engine bots after all.
SEO TIPS
- If you have a media library, step through and check the file names and alt text.
- For new imagery, i.e. blog feature images, consider a template for ensuring they have relevant keywords and a clear description every time new image is added.
Meta titles, tags and descriptions
I’m bet you’ve seen the word ‘meta’ and want to run a mile…and before confusion arises, this is nothing to do with the new name for Facebook or Instagram!
Meta data essentially refers to information about your website which isn’t necessarily plain to see on a webpage itself. It’s sort of like the ‘background information’. For most of us, the main place we see meta data is on a results page:
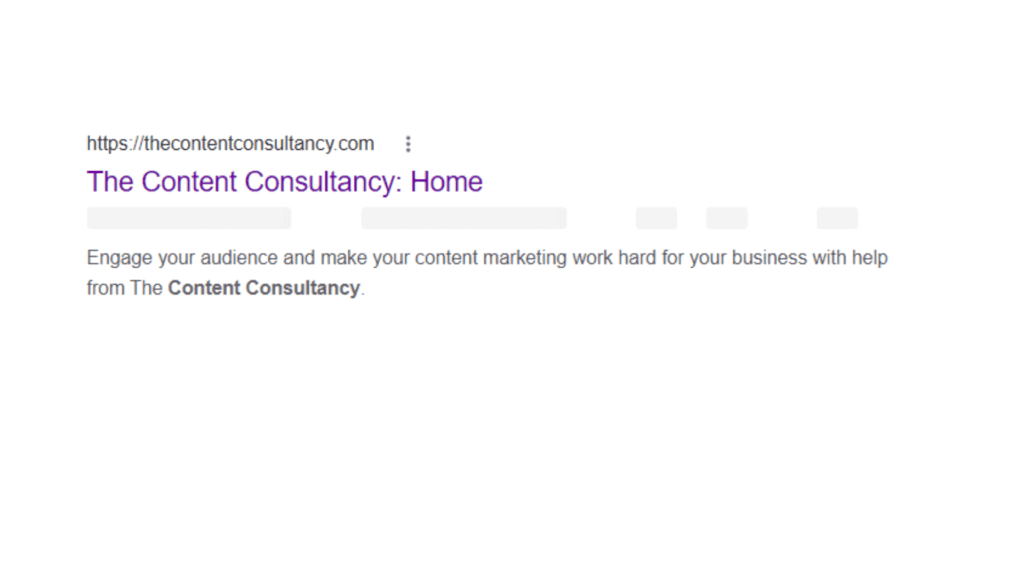
In the image above, you can see the URL (web page address) at the top, then the meta title (in purple) and then the meta description (or excerpt) underneath, which offers a short description of the page. Unfortunately, the page title and the description can be automatically generated…which sounds time saving, but if it’s not checked it may not be working well for your website and SEO.
Errors occur when the meta description is drawn from “any text” the website finds at the top of your page. It finds approximately the first 170 characters and that’s what it shows in a results page. This is also what the search bots are scanning.
This automated text may accidentally include files names or alt text from a banner image at the top of your page, or a even testimonial, if you have one in your ‘above the fold’ content. It can also accidentally ‘grab’ page titles or a heading and run it straight in to an opening sentence, so it doesn’t read very clearly.
This means you don’t end up with a nice clear summary of the page content…but gobbledygook!
SEO TIPS
- Check your meta data for your main pages (and then all pages, when you have time!).
- If you use an SEO plug-in, like Yoast, you are shown a preview and you can write your own excerpt or set what ‘sections’ the excerpt is drawn from. Check them!
- Make sure you write concise clear descriptions for your pages.
Making time for on-page optimisation
I know this blog is packed with a lot of information. It probably seems like there are lots of elements of on-page SEO, as well as lots to do…and it can feel overwhelming. However, what I have found works best for most people is just to do ‘little and often’. Just implement one or two of the tips at a time.
Try to adopt ‘best practice’ going forward too. If you add a new page, consider these six areas.
I love writing websites. I am learning more and more about on-page SEO all of the time. Please feel free to speak to me, if you have any concerns. I can also do a website review (from £105) to help optimise and update your site. I’ll give you lots of recommendations and feedback.
Get in touch to find out more – kate@thecontentconsultancy.com